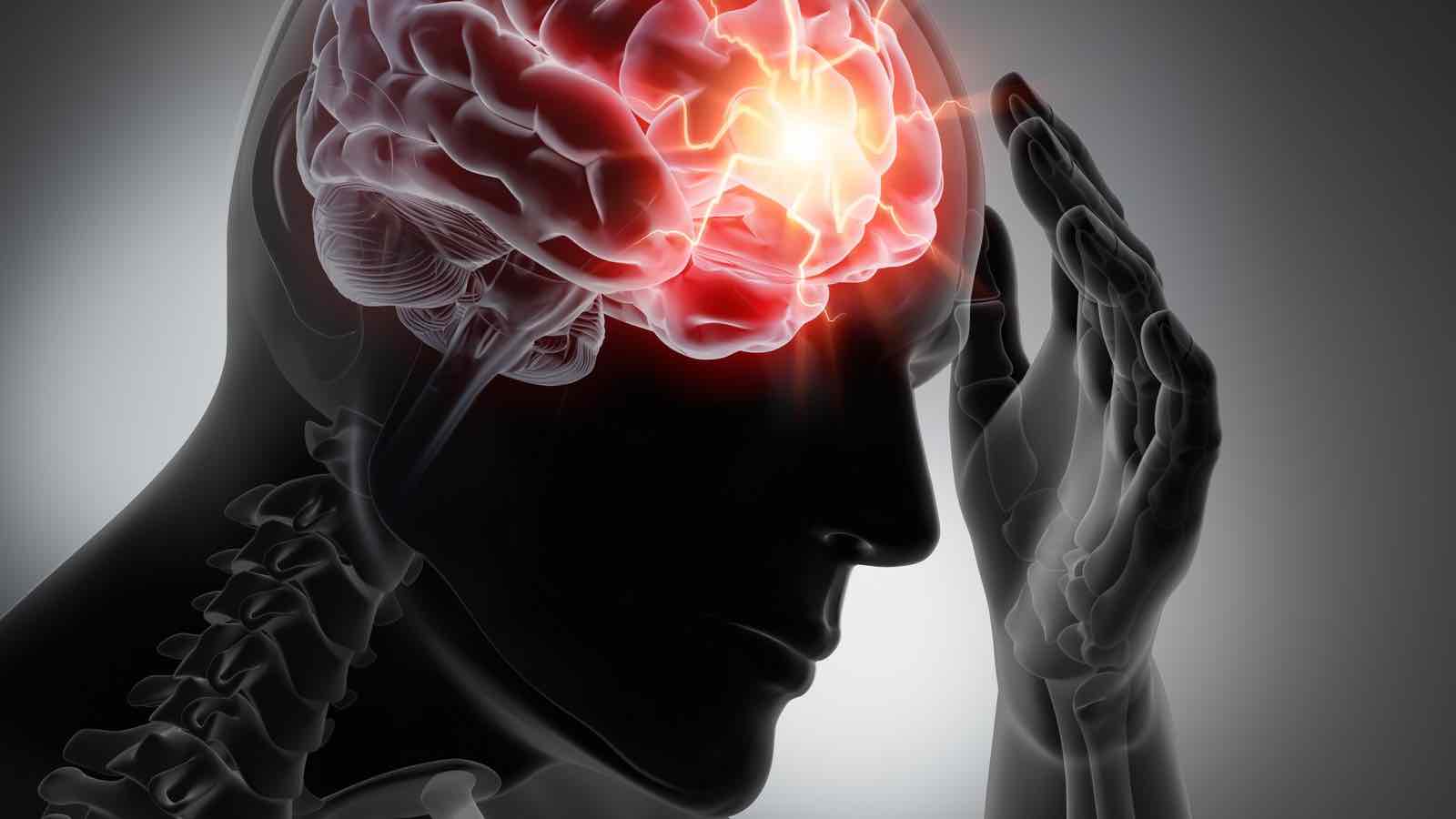
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) often results from a violent blow or jolt to the head or body, causing various physical and psychological effects. While mild cases might lead to temporary brain cell impairment, more severe instances can result in long-term complications, including altered consciousness or even death. Traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) represent a critical public health issue arising from accidents and sports-related incidents. Their profound impact on cognitive, physical, and emotional well-being underscores the need to understand their causes, symptoms, and rehabilitation strategies. This article elucidates the complexities of traumatic brain injuries, focusing on their implications and effective management through physiotherapy and osteopathy.
Symptoms of Traumatic Brain Injury
Traumatic brain injury can have a wide-ranging impact, with some signs or symptoms manifesting immediately after the traumatic event, while others may appear days or weeks later.
Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Symptoms:
Physical symptoms:
- Headache
- Nausea or vomiting
- Fatigue or drowsiness
- Problems with speech
- Dizziness or loss of balance
Sensory symptoms
- Blurred vision
- Ringing in the ears
- A bad taste in the mouth or changes in the ability to smell
- Sensitivity to light or sound
Cognitive, behavioral, or mental symptoms:
- Loss of consciousness for a few seconds to a few minutes
- Dazed, confused, or disoriented state without loss of consciousness
- Memory or concentration problems
- Mood changes or mood swings
- Feeling depressed or anxious
- Difficulty sleeping or sleeping more than usual
Moderate to Severe Traumatic Brain Injury Symptoms:
Physical symptoms:
- Loss of consciousness from several minutes to hours
- Persistent or worsening headache
- Repeated vomiting or nausea
- Convulsions or seizures
- Dilation of one or both pupils of the eyes
- Clear fluids draining from the nose or ears
- Inability to awaken from sleep
- Weakness or numbness in fingers and toes
- Loss of coordination
- Cognitive or mental symptoms:
- Profound confusion
- Agitation, combativeness, or other unusual behavior
- Slurred speech
- Coma and other disorders of consciousness.
Causes of Traumatic Brain Injuries
TBIs can occur due to a multitude of reasons, with the most common being falls, motor vehicle accidents, and sports-related injuries. Additionally, instances of physical assaults or combat-related injuries can also lead to traumatic brain injuries. The impact of sudden acceleration or deceleration forces can cause the brain to collide with the skull, resulting in contusions, hematomas, or diffuse axonal injuries.
Complications
Several complications can occur immediately or soon after a traumatic brain injury. Severe injuries increase the risk of a greater number of and more-severe complications, including:
Altered consciousness: Moderate to severe traumatic brain injury can result in prolonged or permanent changes in a person’s state of consciousness, awareness, or responsiveness. Different states of consciousness include:
- Coma: A person in a coma is unconscious, unaware of anything, and unable to respond to any stimulus. This results from widespread damage to all parts of the brain. After a few days to a few weeks, a person may emerge from a coma or enter a vegetative state.
- Vegetative state: Widespread damage to the brain can result in a vegetative state. Although the person is unaware of surroundings, he or she may open his or her eyes, make sounds, respond to reflexes, or move. It’s possible that a vegetative state can become permanent, but often individuals progress to a minimally conscious state.
- Minimally conscious state: A minimally conscious state is a condition of severely altered consciousness but with some signs of self-awareness or awareness of one’s environment. It is sometimes a transitional state from a coma or vegetative condition to greater recovery.
- Brain death: When there is no measurable activity in the brain and the brainstem, this is called brain death. In a person who has been declared brain dead, removal of breathing devices will result in cessation of breathing and eventual heart failure. Brain death is considered irreversible.
Physical complications:
- Seizures: Some people with traumatic brain injury will develop seizures. The seizures may occur only in the early stages or years after the injury. Recurrent seizures are called post-traumatic epilepsy.
- Fluid buildup in the brain (hydrocephalus): Cerebrospinal fluid may build up in the spaces in the brain (cerebral ventricles) of some people who have had traumatic brain injuries, causing increased pressure and swelling in the brain.
- Infections: Skull fractures or penetrating wounds can tear the layers of protective tissues (meninges) that surround the brain. This can enable bacteria to enter the brain and cause infections. An infection of the meninges (meningitis) could spread to the rest of the nervous system if not treated.
- Blood vessel damage: Several small or large blood vessels in the brain may be damaged in a traumatic brain injury. This damage could lead to a stroke, blood clots, or other problems.
- Headaches: Frequent headaches are very common after a traumatic brain injury. They may begin within a week after the injury and could persist for as long as several months.
- Vertigo: Many people experience vertigo, a condition characterized by dizziness, after a traumatic brain injury. Sometimes, any or several of these symptoms might linger for a few weeks to a few months after a traumatic brain injury. When a combination of these symptoms lasts for an extended period, this is generally referred to as persistent post-concussive symptoms.
Traumatic brain injuries at the base of the skull can cause nerve damage to the nerves that emerge directly from the brain (cranial nerves).
Prevention
To reduce the risk of brain injury, follow these preventive measures:
- Use seat belts and airbags in vehicles.
- Avoid driving under the influence of alcohol or drugs.
- Wear helmets during sports and recreational activities.
- Stay focused on surroundings, avoiding distractions while walking or driving.
Preventing Falls:
For older adults, implement these precautions:
- Install handrails and nonslip mats in bathrooms.
- Remove area rugs and clutter from stairs and floors.
- Ensure proper lighting at home and schedule regular vision checkups.
Preventing Head Injuries in Children:
Protect children from head injuries with these measures:
- Install safety gates at stairways and window guards.
- Use nonslip mats in the bathtub and choose playgrounds with shock-absorbing surfaces.
- Secure area rugs and restrict access to fire escapes and balconies.
Treatment of Traumatic Brain Injury with Physiotherapy and Osteopathy
Physiotherapy and osteopathy play crucial roles in the comprehensive rehabilitation of patients with traumatic brain injuries. Physiotherapy focuses on the restoration of physical function, such as motor skills, balance, coordination, and muscle strength. Through targeted exercises, physical therapists help patients improve their range of motion, alleviate muscle stiffness, and regain motor control. Additionally, physiotherapy assists in the management of pain, vertigo, and headaches, which are common symptoms associated with traumatic brain injuries.
Osteopathy, on the other hand, emphasizes the manipulation of the musculoskeletal system to promote healing, reduce pain, and improve overall physical well-being. Osteopathic techniques can effectively address issues such as headaches, muscle tension, and impaired coordination, often associated with traumatic brain injuries. By employing gentle and non-invasive manual manipulation, osteopathic practitioners aim to enhance the body’s self-healing capabilities and facilitate the restoration of neurological functions.
In conjunction with physiotherapy and osteopathy, the comprehensive range of services offered by York Rehab Clinic presents an advantageous array of treatment options for patients with traumatic brain injuries. Specifically, the clinic’s specialized services, such as shockwave therapy, knee decompression therapy, spinal decompression therapy, acupuncture, and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy, complement the rehabilitative process. Shockwave therapy can aid in the management of chronic pain and musculoskeletal issues, enhancing the overall effectiveness of the treatment plan. Additionally, knee and spinal decompression therapies contribute to alleviating pain and promoting the regeneration of injured tissues, facilitating the recovery process for patients with traumatic brain injuries.
Furthermore, acupuncture, known for its ability to alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and improve neurological function, can significantly complement the physiotherapy and osteopathy treatments. Acupuncture can effectively address symptoms such as headaches, sensory disturbances, and cognitive impairments, thereby enhancing the overall well-being of patients during their recovery journey.
By integrating these diverse services, York Rehab Clinic aims to provide comprehensive and individualized care for patients with traumatic brain injuries, emphasizing a holistic approach that addresses both physical and neurological rehabilitation needs. With a focus on personalized treatment plans tailored to each patient’s specific requirements, the clinic strives to promote optimal recovery and improved quality of life for individuals navigating the challenges posed by traumatic brain injuries.
Conclusion
In conclusion, traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) present complex challenges, with wide-ranging physical, cognitive, and emotional implications. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and potential complications associated with TBIs is crucial for effective management and rehabilitation. Physiotherapy and osteopathy, in conjunction with specialized services provided by York Rehab Clinic, play instrumental roles in the holistic treatment of traumatic brain injuries. Through a multidisciplinary approach that addresses physical rehabilitation, pain management, and neurological function enhancement, patients can benefit from a comprehensive and tailored treatment plan that aims to promote optimal recovery and improve overall quality of life. By combining expertise, cutting-edge therapies, and personalized care, York Rehab Clinic remains committed to supporting individuals in their journey towards recovery from traumatic brain injuries.